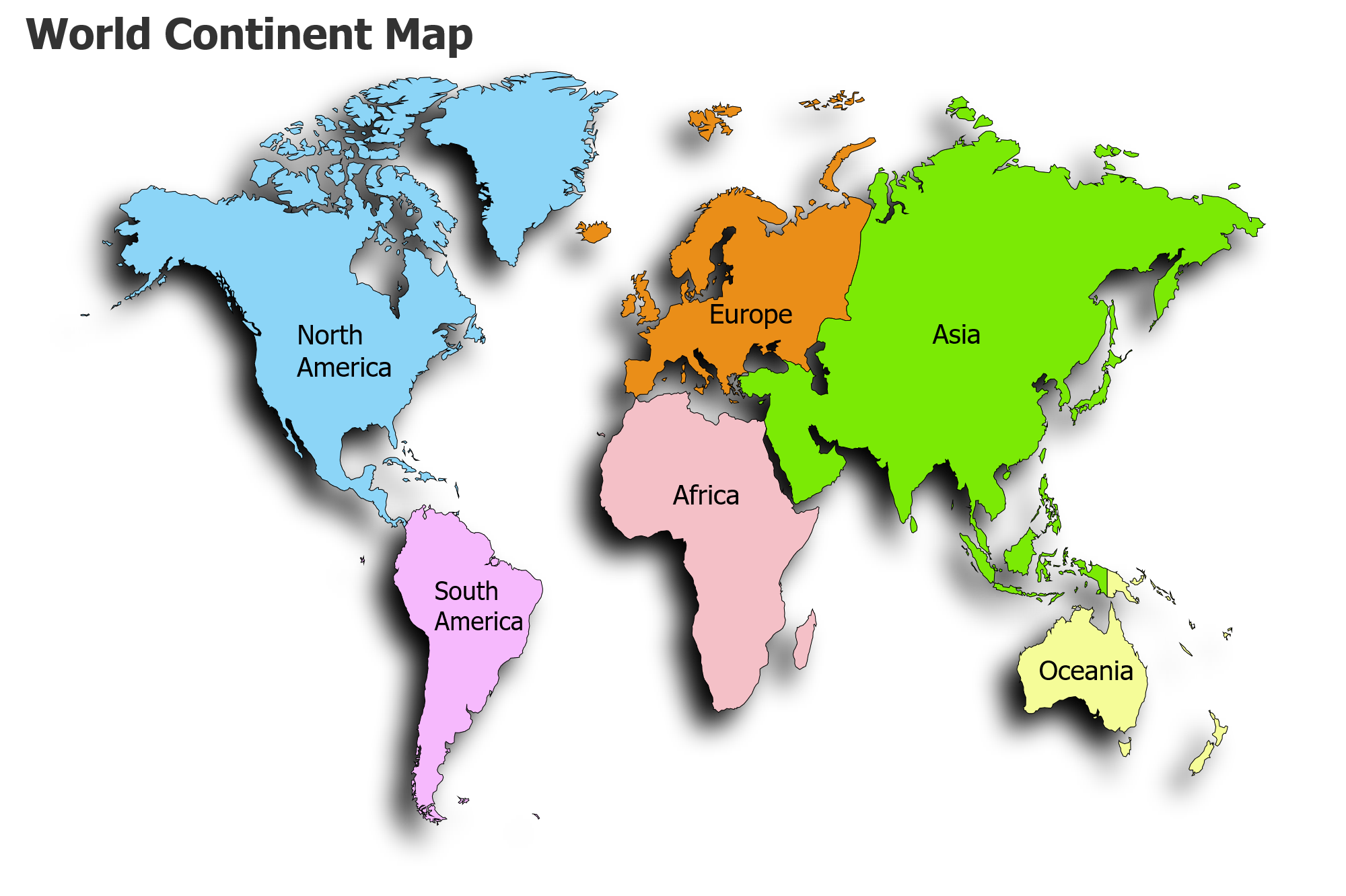
What is a continent?
The world has two major surfaces: land and water. Land area is further divided into 7 larger parts known as the Continent and the water surface is divided into 5 oceans.
A continent is one of the several large land masses usually consisting of multiple countries. There is no specific definition of continent. The most agreed definition is “continents are understood to be large, continuous, discrete masses of land, ideally separated by expanses of water.”
How many continents are there in the world?
Currently the world is divided into 7 continents. The seven continents of the world are Arfica, Asia, Europe, Oceania/Australia, North America, South America, Antarctica.
However there are multiple continent models:
Four continent: Afro-Eurasia, Americas, Antarctica, Australia
Five continent: Africa, Eurasia, Americas, Antarctica, Australia
Six continent: Africa, Europe, Asia, Americas, Antarctica, Australia
Seven continent: Africa, Europe, Asia, North America, South America, Antarctica, Australia
- Seven continent model is taught in most english speaking countries.
- Six continent model is taught in eastern europe, russia, japan
Largest and Smallest continents of the world
List of continents by size(largest to smallest)
| SL | Name | Area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Asia | 44579000 |
| 2 | Africa | 30370000 |
| 3 | North America | 24709000 |
| 4 | South America | 17840000 |
| 5 | Antarctica | 14000000 |
| 6 | Europe | 10180000 |
| 7 | Oceania /Australia | 8600000 |
List of continents by Population(highest to lowest)
| SL | Name | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Asia | 4545133000 |
| 2 | Africa | 1287920000 |
| 3 | Europe | 742648000 |
| 4 | North America | 587615000 |
| 5 | South America | 428240000 |
| 6 | Oceania /Australia | 41261000 |
| 7 | Antarctica | 4490 |
Highest and Lowest Points of the continents
Tables below contains the list of highest peaks and lowest points by continents
Highest points by continents
| Highest Point | Continent | Height(Meter) | Country/Territory |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mount Everest | Asia | 8,848 | Nepal , India, China |
| Aconcagua | South America | 6,960 | Argentina |
| Denali | North America | 6,198 | United States |
| Mount Kilimanjaro | Africa | 5,895 | Tanzania |
| Mount Elbrus | Europe | 5,642 | Russia |
| Vinson Massif | Antarctica | 4,892 | N/A |
| Puncak Jaya | Australia | 4,884 | Papua, Indonesia |
Lowest points by continents
| Lowest Point | Continent | Height(Meter) | Country/Territory |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dead Sea | Asia | −427 | Israel, Jordan, Palestine |
| Lake Assal | Africa | -155 | Djibouti |
| Laguna del Carbón | South America | −105 | Argentina |
| Death Valley | North America | -86 | United States |
| Deep Lake | Antarctica | -50 | None |
| Caspian Sea | Europe | -28 | Russia |
| Lake Eyre | Australia | -15 | Papua, Indonesia |
Number of countries in a continent
Each continent consists of multiple countries except Antarctica.
- Africa has total 54 countries
- Europe has total 47 countries
- Asia has total 44 countries
- North America has total 23 countries
- Oceania /Australia has total 14 countries
- South America has total 12 countries
- Antarctica has total 0 countries
It's worth noting that the number of countries in each continent can vary depending on the definition and classification used, and there may be other territories or regions that are sometimes included as part of a continent.
Summary
Asia houses some of the richest nations in the world. The tiny country Qatar on the Arabian peninsula is on of the richest nations in the world due to its income from oil exploration and the petroleum industry. Saudi-Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain are also among richest countries in the world due to their oil reserves.